Table of Contents
Your car battery is the heart of your vehicle’s electrical system, providing the necessary power to start the engine and run essential components. Understanding car battery voltage is crucial for diagnosing issues, maintaining performance, and preventing breakdowns. Understanding its significance is paramount for maintaining efficiency and reliability in modern automobiles. Before Discovering the more about this fascinating topic by reading on! Here is the article to must read if you are facing any problem or want to know about battery sizes.In this guide, we’ll break down what you need to know about car battery voltage, how to test it, and what different voltage readings indicate.
Understanding Car Battery Voltage
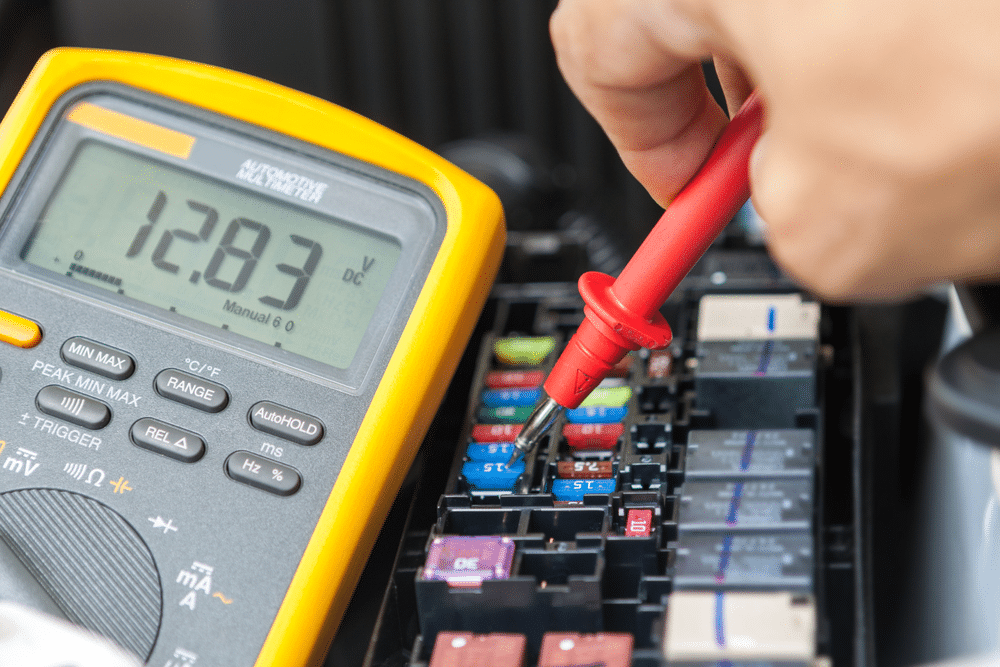
A car battery typically operates at 12 volts (V), but its actual voltage can vary depending on the state of charge, temperature, and whether the engine is running or off. The key voltage levels to understand are:
- Fully Charged Battery – Around 12.6V to 12.8V when the engine is off.
- Partially Charged Battery – Between 12.4V and 12.6V, indicating some discharge but still functional.
- Low Battery – Below 12.4V, meaning the battery may need recharging.
- Dead Battery – Below 12.0V, likely unable to start the car.
When the engine is running, the alternator increases the battery voltage to about 13.7V to 14.7V, ensuring the battery remains charged while supplying power to the vehicle.
Different Types Of Voltages
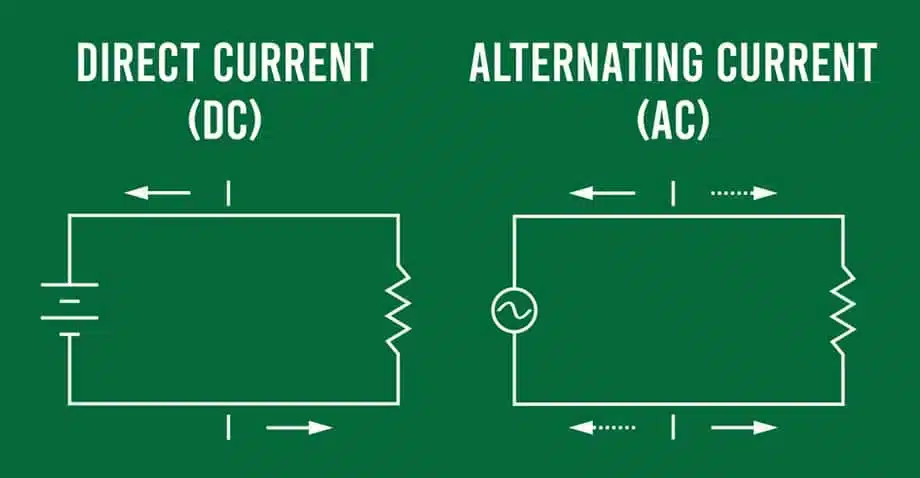
There are two types of voltages, and here is an explanation for both.
AC voltage
The important thing in Car Battery Voltage is The voltage of an alternating current (AC) is a type of electrical energy that varies continuously in direction and magnitude over time. The periodic movement of AC voltage along a conductor differs from that of Direct Current (DC), which flows continuously in one direction. Typically, AC voltage follows a sine wave pattern. The frequency at which this oscillation happens is usually 50 or 60 Hertz (Hz). It depends on the power grid standards in the area.
DC voltage
Direct current (DC) voltage is an essential component of many electrical systems, including those used in automobiles and car batteries. Knowing the DC voltage of automobile batteries is essential when delving into this topic. A car battery typically runs at a nominal voltage of 12 volts, which can vary slightly based on the battery’s condition and other variables. The 12-volt standard is now widely used in car design, powering everything from the entertainment system and lights to the ignition system.
Manual Cars Voltage
Manual cars typically run on a 12-volt electrical system like automatic cars. However, this voltage powers components such as the starter motor, lights, ignition system, radio, and air conditioning accessories. The voltage is supplied by the car’s battery, which is recharged by the alternator while the engine is running.
Automatic Cars Voltage
Automatic automobiles and other electric vehicles (EVs) usually rely on high- Car Battery Voltage systems. Furthermore, the precise voltage may differ based on the manufacturer and model, but it often ranges from several hundred to over 800 volts for contemporary EVs. While other electric cars may have voltages between 400 and 600 volts. The Porsche Taycan, for instance, runs on a system voltage of 800 volts.The electric motors and other systems in the car require these high voltages to have enough power.
How to Test Car Battery Voltage
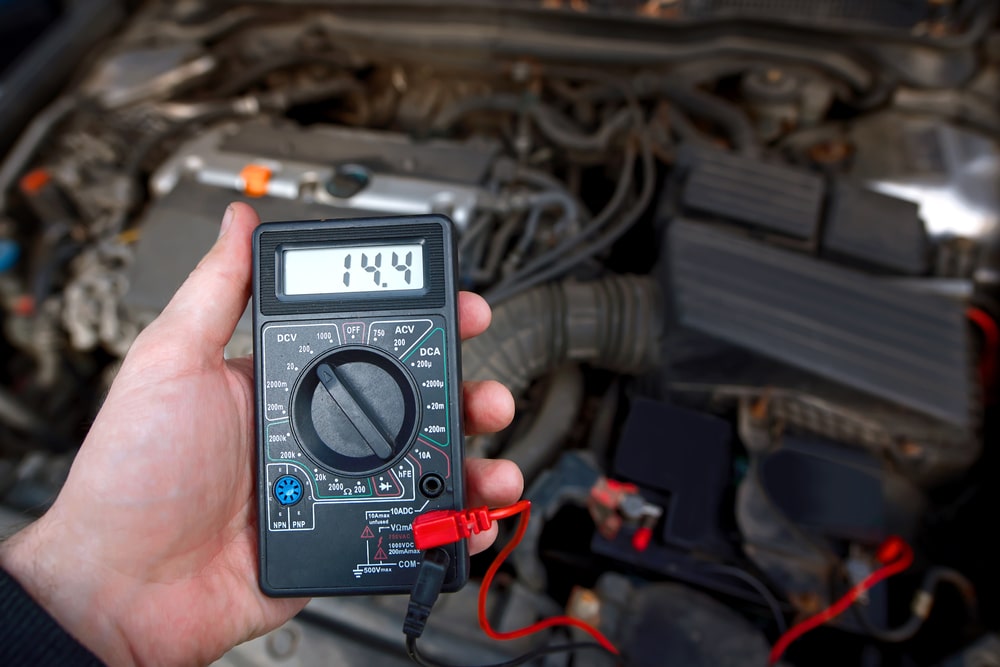

Checking your car battery voltage is simple with a multimeter. Follow these steps:
- Turn Off the Engine – To get an accurate resting voltage reading.
- Set the Multimeter – Adjust it to DC voltage mode (V with a straight line).
- Connect the Probes – Red to the positive terminal (+) and black to the negative terminal (-).
- Read the Voltage – Compare it with the values listed above.
If the voltage is too low, consider charging the battery or seeking professional assistance.
Why Car Battery Voltage Matters
- Prevents Unexpected Failures – Regular voltage checks help you avoid being stranded with a dead battery.
- Ensures Efficient Performance – A properly charged battery maintains consistent performance.
- Extends Battery Life – Preventing deep discharges can help your battery last longer.
By monitoring car battery voltage, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and avoid costly repairs. If your battery consistently reads low, it may be time for a replacement.
Conclusion
Understanding car battery voltage is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s performance and reliability. By regularly checking your battery’s voltage, you can prevent unexpected failures, ensure efficient operation, and extend its lifespan. A healthy battery should read 12.6V to 12.8V when fully charged and 13.7V to 14.7V while the engine is running. If you notice consistently low readings, it may be time to recharge or replace your battery.
Regular maintenance and monitoring will keep your car running smoothly and help you avoid costly repairs. Stay proactive, and your battery will continue to power your vehicle efficiently!
